In our day to day life we came across various engineering problems. Once we face these engineering problems few questions will come in our mind like How to resolve it? What are different methods? Which is the simplest or best method?
In this paragraphs, we will discuss various methods to solve any engineering problems & their comparison with each other. There are three basic methods to solve any engineering methods.
- Analytical Methods
- Numerical Methods
- Experimental methods
1. Analytical Methods:
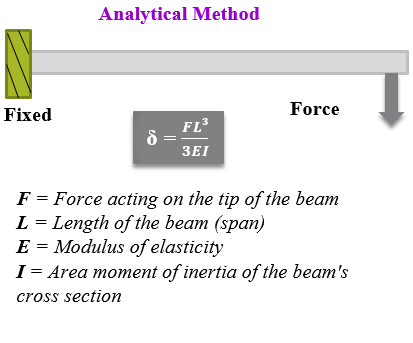
The analytical method is most widely used in curriculum study as well as used by industrial designers to solve the engineering problems. It is a classical approach which gives 100 % accurate results. This approach is also referred to as hand calculations; as in this method various mathematical equations & functions are used to find output variables & derive closed form solutions. This method is mainly applicable for simpler problems like cantilever and simply supported fixed beams, etc.
Though the analytical approach is 100 % accurate, it could also give approximate results if the solution is not closed form. An equation is said to be a closed-form solution if it solves a given problem in terms of mathematical operations & functions from a given generally accepted set. For example, an infinite sum would generally not be considered closed-form.
2. Numerical Method:
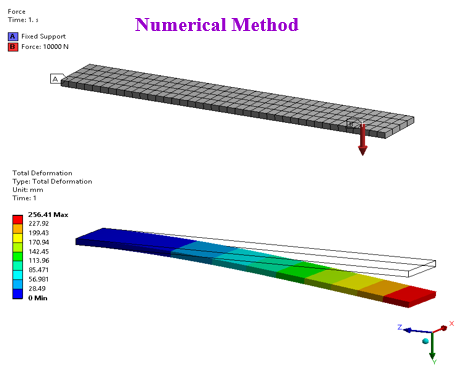
When we come across more complex problems, in which both analytical and experimental methods do not work, numerical methods are driving the solutions. CAE engineers or analysts most widely use numerical methods to solve their engineering problems. This numerical method uses computational techniques through simulation software’s & large infrastructures, etc. Numerical methods do not need physical models or prototypes, it builds mathematical models to replicate real life complex problems and while doing so, several assumptions were made to simulate the analysis. Therefore, the results from this method are approximate. So, you cannot believe the results blindly and hence, sometimes sanity checks are needed to validate the simulation either by hand calculations or by physical testing, etc.
The four common numerical methods used to solve engineering problems are:
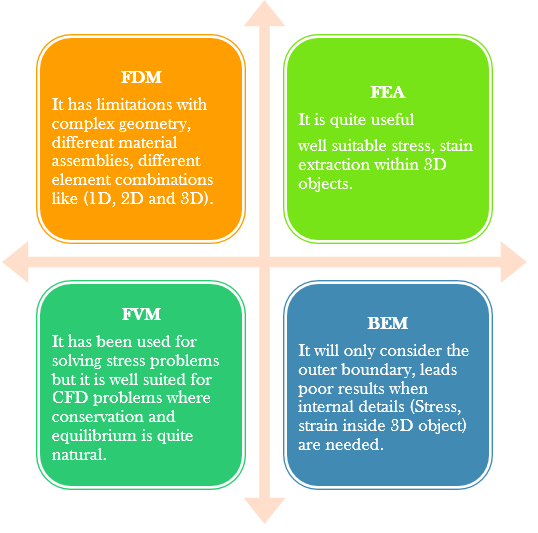
- Finite Element Method:
- The Finite Element Method (FEM) is a popular numerical technique used to determine the approximated solution for a partial differential equation (PDE).
- Applications: Linear, nonlinear, buckling, thermal, dynamic, and fatigue analysis
- Boundary Element Method (BEM):
- Powerful and efficient technique to solve acoustics or NVH problems. Just like FEA, it also requires nodes and elements, but it only considers the outer boundary of the domain. So when the problem is of a volume, only the outer surfaces are considered. Similarly if the domain is of an area, then only the outer periphery is considered. By doing so it reduces the dimensionality of the problems by one degree resulting in faster problem solving. BEM is often more efficient than other methods in terms of computational resources for problems where there is a small surface or volume ratio.
- Applications: Acoustics, NVH
- Finite Volume Method (FVM):
- The FVM method representing and evaluating partial differential equations as an algebraic equations method is used in many computational fluid dynamics packages. It is very similar to FDM, where the values are calculated at discrete volumes on a generic geometry. The advantage of this method is that it is easily formulated to allow for unstructured meshes.
- Applications: CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) and Computational Electromagnetic
- Finite Difference Method (FDM):
- It uses Taylor’s series to convert a differential equation to an algebraic equation. In the conversion process, higher order terms are neglected.
- It is used in combination with BEM or FVM to solve thermal and CFD coupled problems.
Can we solve the same problem with all Numerical methods?
The answer is YES, but substantial differences exist between this method in terms of accuracy, ease of programming & computational time, etc.
3. Experimental Method:
Experimental method is also known as physical testing. It is one of the most reliable methods and widely used in industry for product prototype testing.
In this method, the product or component is tested in real time operating conditions & actual measurement were reported. So in order to use this method, you will need a physical prototype of the product or structure you want to be analyzed. Only one prototype testing is not sufficient, for final outcome of analysis 3 to 5 prototype testing is required. Due to this, the experimental method is time consuming, requires expensive physical setup which results in additional cost rather than actual products.
Physical testing is performed with the help of various measuring equipment like strain gauges, different sensors, measuring devices like accelerators, etc. to calculate various parameters of the experiment. Examples: Compressor manufacturers are doing prototype testing to mitigate the vibration levels on prototypes. Here, different accelerators are placed at various point on prototype and acceleration levels are measured for operational loads.
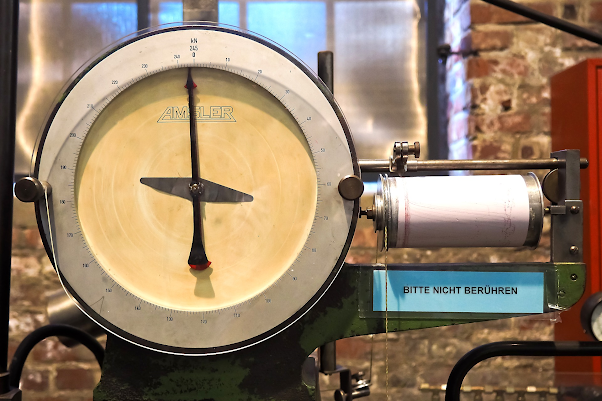

Below images shows the simple cantilever beam problems solution by three different methods approach.