In FEA, when two separate surfaces touch each other such that they become mutually tangent then they are said to be in “contact”. Contact conditions are created when an assembly is imported into the application and it detects that two separate bodies (solid, surface, and line bodies) touch one another (they are mutually tangent). In such contact problems, the common question you came across is, how to decide which is master and slave surface ? or which is contact and target surface? Most of the time autocontact, defines master and slave surface for us. But sometimes, when complex FEA problems such as nonlinearity involve or few manual contact required to define, we need to make a decision which should be master or slave surface. In general, the master surface is on the touched body or the body with the moving body will come in contact, while the slave surface is on the touching body or on the moving body which will form contact with another body, as shown in figure 1.
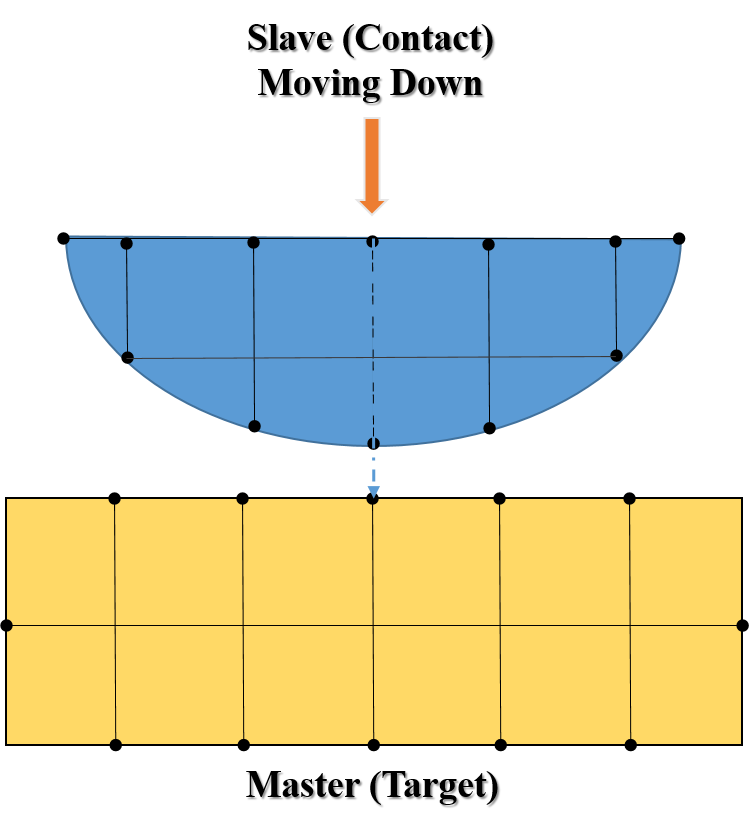
Let’s first discuss why there are two different definitions for contact surfaces like Master & Slave or Contact & Target. As we know there are different FEA software available in the market. Contact & target terminology is used in ANSYS software while master and slave is used in Abaqus FEA Package. The master is equivalent to target and slave is equivalent to contact.
Types of Contact Surfaces Behavior
There are three different contact behaviors are available in ANSYS software: Asymmetric, Symmetric, Auto-asymmetric
Asymmetric Behavior: In Asymmetric Behavior, only the contact surfaces are constrained from penetrating the target surfaces. In case of program controlled , the contact behavior is set to Flexible-Rigid bodies.
Symmetric Behavior: In Symmetric behavior, the contact surfaces are constrained from penetrating the target surfaces and the target surfaces are constrained from penetrating the contact surfaces. In case of program controlled, the contact behavior is set to Flexible-Flexible bodies that are scoped to a Nonlinear Adaptive Region..
Auto Asymmetric: In Auto Asymmetric Behavior, The program evaluates the contact region and chooses which surface should be meshed with contact elements and which should be meshed with target elements. In case of program controlled , the contact behavior is set to Flexible-Flexible bodies.
Furthermore, there are few guidelines to decide which one is master and slave surface or which one is contact and target surface, discussed in the paragraphs below.
Guidelines for Contact Surfaces Selection, Asymmetric Behavior:
- If one surface has a coarse mesh and the other a fine mesh, then the target surface should be the surface with Corse mesh.
- If a convex surface comes into contact with a flat (or concave) surface, then target surface should be flat (or concave) surface.
- If one surface is higher order and the other is lower order, then the target surface should be with lower order surface.
- If one surface is stiffer than the other, the stiffer surface should be the Target surface.
- If one surface is larger than the other, the larger surface should be the Target surface.
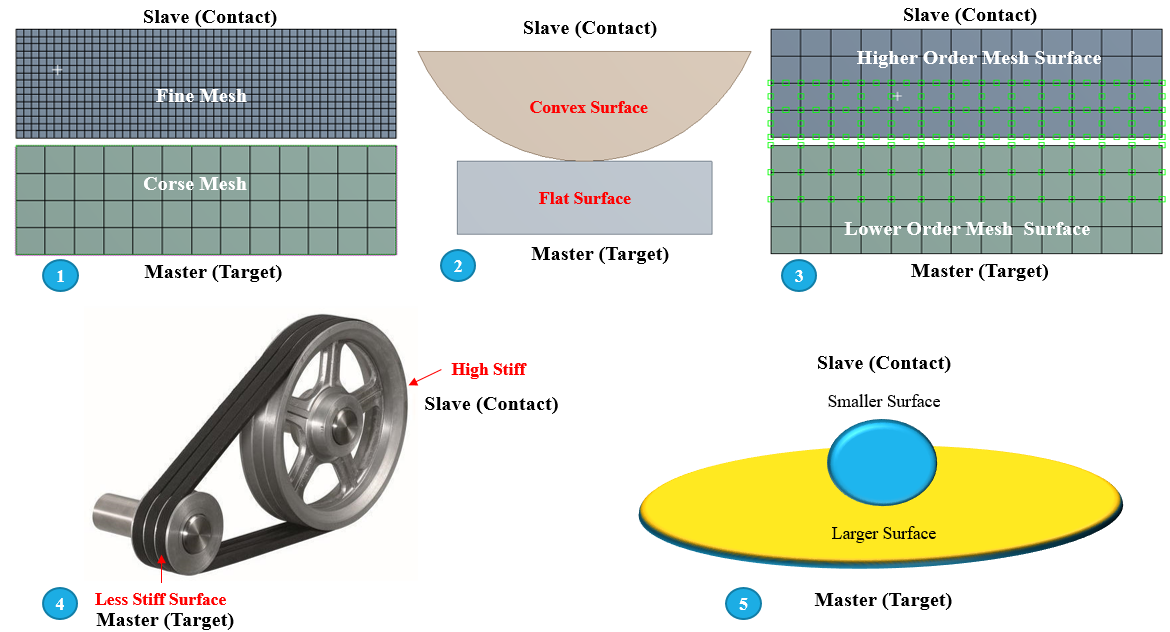
These guidelines are defined for asymmetric behavior, but you can even use this for any other behavior type with other FEA software’s also.
References:
- ANSYS Help Manuals, 2019.
Summary:
This blog presents the Contact definition, Master & Slave surface or Contact & target surface definitions, Types of contact behavior & guidelines for contact surface selection, etc.
